Cooling, Heating and Power Engineering
Heat Pump Engineering
Common heat pumps in engineering can be divided into: water source heat pumps (sewage source heat pumps), ground source heat pumps, air source heat pumps and absorption heat pumps (Class I, Class II), etc.
Scope of application: Water source heat pump and ground source heat pump can be widely used in centralized heating and refrigeration systems in hotels, office buildings, schools, shopping malls, villas and residential areas. Air source heat pumps are generally used in small heating and cooling systems, especially in single buildings. Absorption heat pumps are mainly used in various industrial waste heat recovery and heating fields, as well as thermal power plants and other places.
Cases

Zhongxing-Shenyang Commercial Building
Overview: Zhongxing Building has a construction area of 233,000 square meters; Thermal index: 44W/m², Cold index: 110W/m²; The water output of a single well is 160 m³/h
Technical form: water source heat pump + electric boiler + water heat storage + ice cold storage.
Economic indicators: 15%-30% reduction in operating costs of conventional cold and heat source systems compared with the same type of places.

Shenyang Polytechnic College
Overview: construction area of 120,000 m²; The sewage trunk channel flowing through the college is used as the sewage heat source of the system, with a flow rate of 230T/h and a sewage temperature of more than 13℃.
Technical form: sewage source heat pump + ice storage system + wide channel sewage heat exchanger.

The Second People's Hospital of Liaoyang City
Overview: The water source heat pump system provides cooling, heating and domestic hot water for the 54,000 m² building.
Technical form: water source heat pump + groundwater natural cold source
Economic indicators: 30%-40% reduction in operating costs compared to conventional cooling and heating source systems in similar places
Combined Cooling Heating and Power
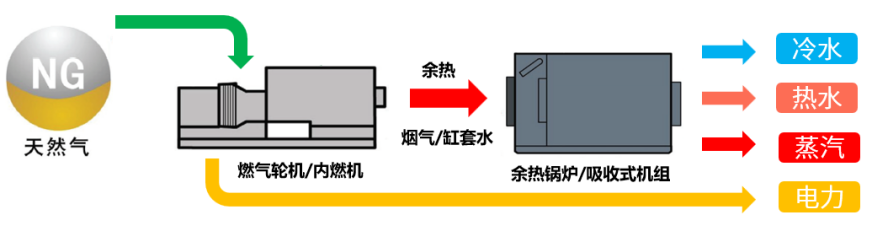
Combined Cooling Heating and Power(CCHP) : refers to the distributed energy supply system that uses natural gas clean energy as fuel and applies energy conversion equipment including various thermal power generator sets and waste heat utilization units such as gas turbines, gas internal combustion engines, and micro-combustion engines to provide users with various load requirements of cold, heat and electricity.
Advantages of CCHP
Energy Demand-side Management
Using natural gas and residual heat, the power generation and energy supply system is built near the user's energy management system, which greatly reduces the power loss of transmission.
Supply of Multiple Energy Types
According to the needs of users, electricity, heating, cooling, steam and domestic hot water can be supplied at the same time.
Cascade Utilization of Energy
Improve the comprehensive benefit of energy, and the utilization rate of heat energy can reach 70%-90%.
Typical Systems & Applications
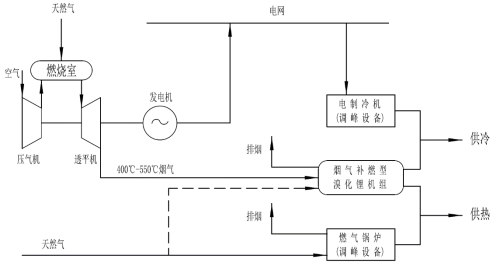
System composition: Gas turbine + Flue gas (refueling) lithium bromide unit + Peak shaving equipment
Energy supply: Electricity + Cooling + Heating
Applications: Data centers, computer rooms and other places with high-power electrical equipment and perennial demand for cooling load.
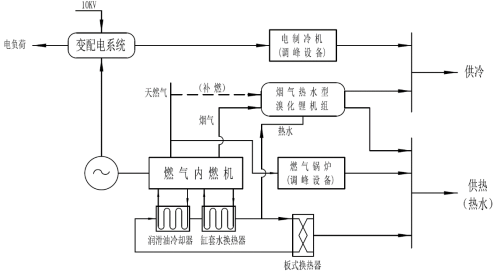
System composition: Gas internal combustion engine + Flue gas (hot water) absorption air conditioning unit (refueling) + Peak shaving equipment
Energy supply: Electricity + Cooling + Heating
Applications: Suitable for occasions with a large amount of domestic hot water and swimming pool heating, and is also suitable for matching heat pump systems.


